
Blood loss is often the leading cause of death from trauma. As a solution, scientists have developed patches that quickly stop the blood by accelerating the clotting process. The first experiments showed that the time of blood loss is reduced by almost 10 times.
Scientists from the University of Pennsylvania presented a patch based on hemostatic microneedles to quickly stop bleeding. The new patch can be compared to hydrogel technology for the treatment of bleeding wounds, but unlike hydrogel, it does not require medical expertise to use and is designed for easy use by anyone.
The bandage is similar to an ordinary adhesive plaster, but due to its properties, it can quickly stop blood loss. For example, biocompatible and biodegradable needles increase surface contact with blood and accelerate the blood clotting process. In addition, the needles improve the adhesive properties of the patch due to mechanical adhesion, which helps to close the wound.
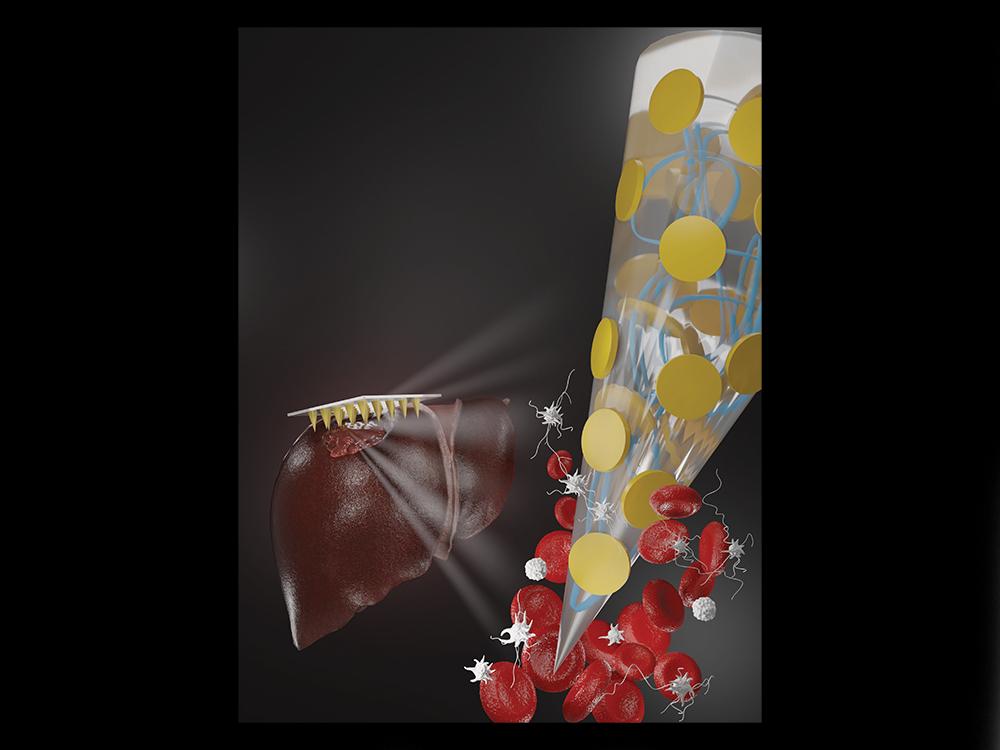
In laboratory experiments, the use of the patch reduced the blood clotting time from 11.5 minutes to 1.3. In rat models, liver bleeding was reduced by more than 90%.
‘These 10 minutes can be the difference between life and death,’ commented the author of the work, Amir Sheikhi. The obtained data demonstrate a great potential for application in humans, since often it is not the injury itself, but the loss of blood that becomes the main cause of a person’s death. Testing of technology properties continues.
Meanwhile, other scientists have developed a patch to continuously track cancer through the skin. It works continuously in deep tissues and is able to identify signs of disease.

