
The power consumption of video cards will reach 600-700 W by 2025 — AMD forecast
Recent rumors about upcoming consumer graphics card models have raised concerns about their increased power consumption. And while AMD and NVIDIA have yet to reveal the full specifications of the next generation of graphics cards (Radeon RX 7000 and GeForce RTX 40 series) expected later this year, Lisa Su’s “red” team this week released some alarming numbers in its roadmap on near future.
As engineers increasingly face the limits of Moore’s Law, consumers worry that the TDP of future GPUs could reach insanely high levels. NVIDIA’s next flagship graphics card (potential RTX 4090), expected later this year, is rumored to draw up to 600W. By comparison, the current top-of-the-line green card for the consumer market, the 3090 Ti, consumes 450 watts of power.
An interview with AMD senior vice president Samuel Nafziger that appeared this week on VentureBeat included renderings showing the company’s expectations for near-future hardware. The top manager assures that AMD will be able to realize its ambitions to improve energy efficiency over the next few years, but the graph clearly shows a disappointing trend — the increase in GPU energy consumption.
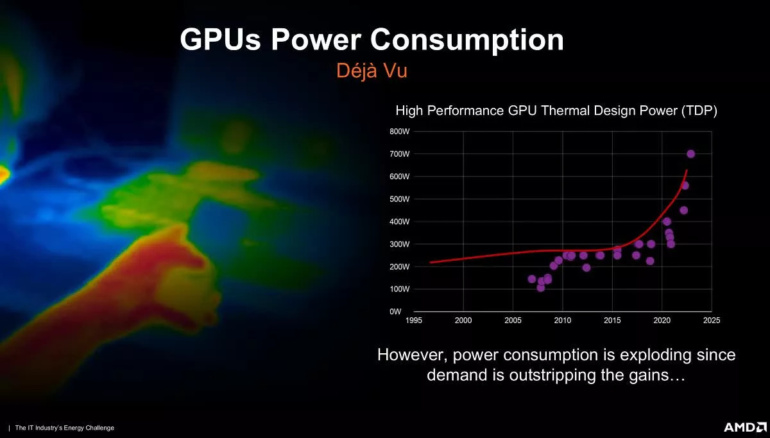
If 600-watt models don’t appear in the next generation of desktop graphics accelerators, then such models, based on AMD graphics, will follow. That is, after one generation. It shows a sharp increase in GPU power consumption around 2018, followed by a jump to 600W and then 700W by 2025.
The slide does not have any additional markings that would signal that it belongs only to the highest-end hardware. Currently, the most popular graphics cards on the market (budget to mid-budget models) consume significantly less, but the trend is clear – future mainstream GPUs will require more power as the chips become more complex and the industry leans into the technological capabilities of semiconductor manufacturing.
Mr. Naffziger emphasized that with the new graphics cards, AMD can provide an increase in performance at the level of consumer expectations and at the same time solve the problem of power consumption. It is predicted that the 3rd generation RDNA GPUs will increase the performance per watt by at least one and a half times compared to their predecessors.
AMD also relies on the Infinity Cache buffer — this technology is promoted by the manufacturer as one of its unique advantages. At the same time, Naffziger singles out chiplet design as an area where AMD has overtaken NVIDIA. Previously, AMD already managed to test the approach with multi-chip GPUs in accelerators for data centers (Instinct MI200 line) and will now extend it to gaming video adapters.
If recent rumors are to be believed, due to the surplus of GeForce RTX 3000 models on the market and the mass sale of used video cards by miners after the fall of cryptocurrencies, NVIDIA will postpone the release of GeForce RTX 4000 series video cards from October to December. The Radeon RX 7000, which will compete with the GeForce RTX 4000, will most likely be released around the same time.

